
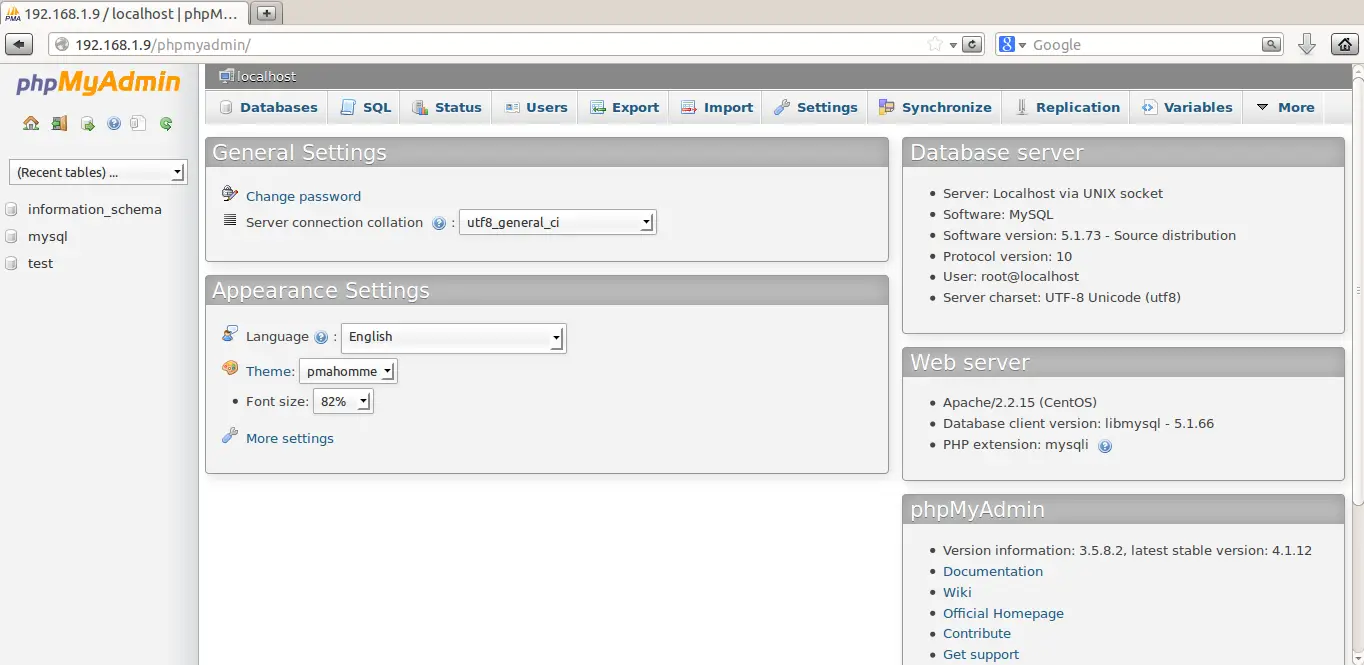
Step 2: Secure your phpMyAdmin InstanceĪt this point, the phpMyAdmin instance installed on our server should be fully functional. In your web browser, navigate to your server’s domain name or public IP address followed by /phpMyAdmin: Log in to the interface as root or using another username and password. With that, our phpMyAdmin installation is complete. Restart Apache: $ sudo systemctl restart apache2 To finish setting Apache and PHP to interact with phpMyAdmin, the next task in this section of this guide is to explicitly activate the mbstring PHP extension, which you can achieve by typing: $ sudo phpenmod mbstring The installation procedure places the phpMyAdmin Apache configuration file in the /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/ directory, where it is immediately read. On Ubuntu, When requested, you should choose apache2.
Setup phpmyadmin ubuntu install#
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install phpmyadmin php-mbstring php-zip php-gd php-json php-curl To begin, we will install PhpMyAdmin from the distro default repository.
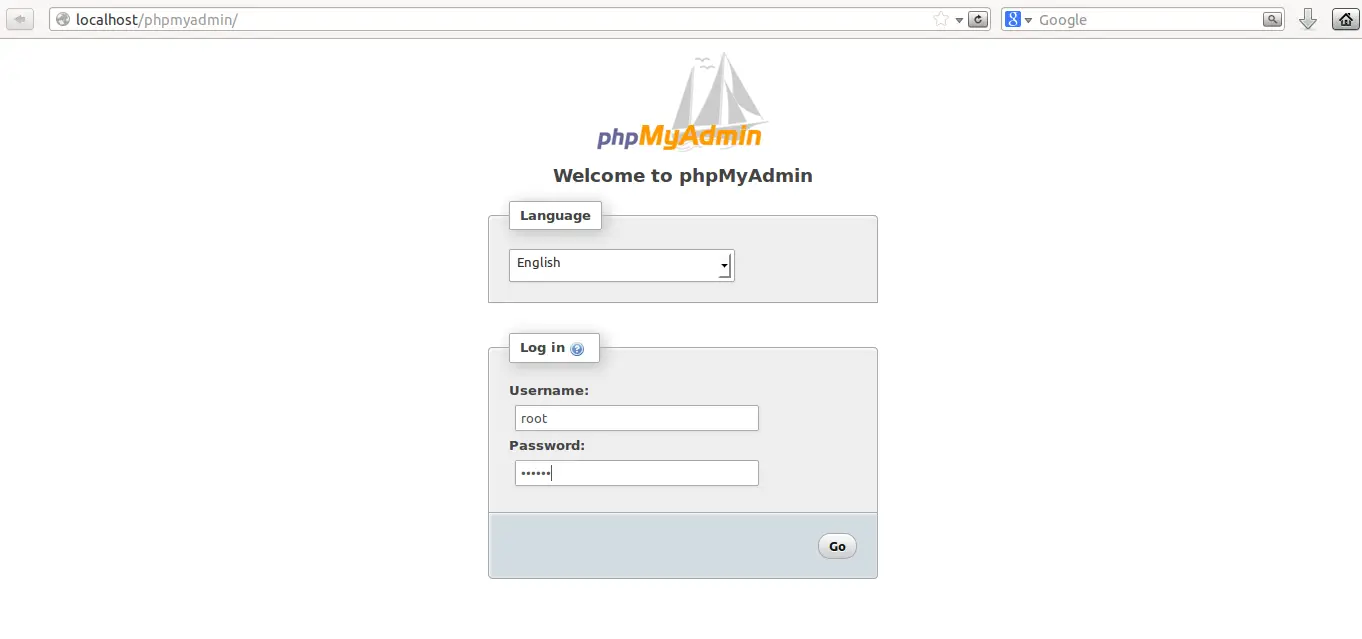
Once you’ve completed these steps, you’re prepared to start this guide. If you do not already have a domain established with an SSL/TLS certificate, you may use this method to create one, securing Apache with Let’s Encrypt on Ubuntu.
Setup phpmyadmin ubuntu software#
You can follow this guide on installing a LAMP stack to set this up.įinally, while utilizing software like PhpMyAdmin, there are essential security issues to be aware of because it: Ubuntu server with a non-root administrative user with sudo privileges.
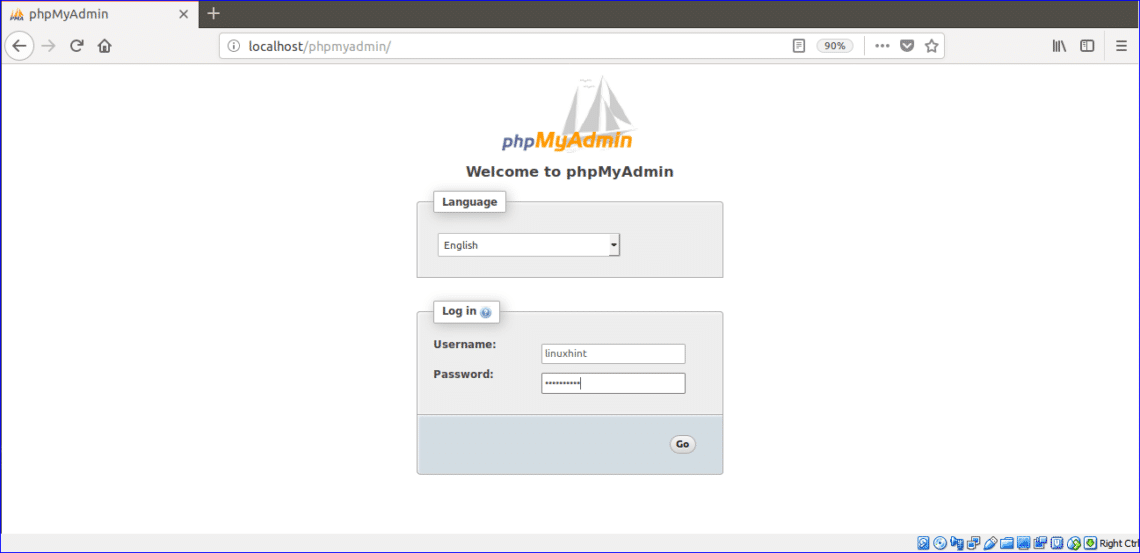
We’ll go over installing and securing PhpMyAdmin in this guide, so you can use it to manage your databases on an Ubuntu system without risk. To enable user interaction with MySQL via a web interface, PhpMyAdmin was developed. Although many users require a database management system like MySQL’s functionality, they might not feel at ease interacting with the system only through the MySQL command line client.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
